|
Environment; I'll put down a few things here which is exactly what I'm talking about and safety and security, again, I'll talk about it a little bit later as we go along, but we are in a very fortunate condition because we deal with thermal energy, thermal systems, just look at where this goes – from manufacturing, energy systems, cooling systems, environment, safety system, aerospace. You don't have too many aerospace systems without thermal sciences. Transportation, whether it's an automobile or a train. Air-conditioning systems, heat transfer equipment. We are essentially almost in every domain what the society needs or what the society uses, but still when you look at an overall impact on the society on issues which are of critical importance to the world, we don't seem to have the standing that we should have. Therefore, I think this question is very, very important, how can we meet this challenge? What should we be doing in order to make a major effect?
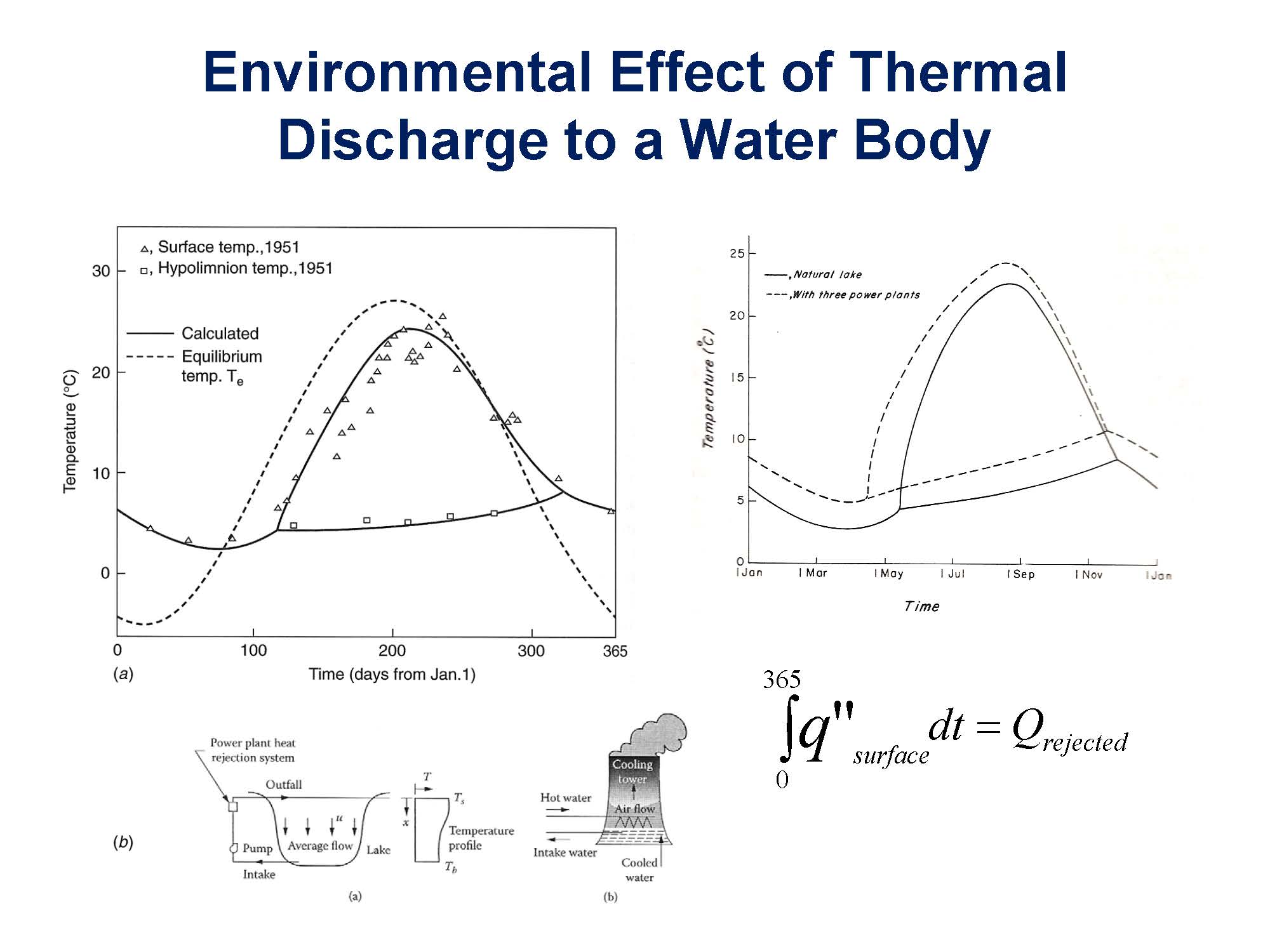
Energy; certainly there are important considerations and I have put down a few of them here. The fossil fuels, of course, have been the classical domain, but the renewables – we have gone into them, but probably not to the extent that we should and we still have many areas, particularly in storage, even in solar, even in photovoltaics as you well know, we do manufacturing, so we could talk about making solar cells much cheaper so that they become a possibility for many people in the world. Environment, unfortunately, is one of the cases which I feel we have been sidelined. We did a lot of work in local pollution. If I go back to the 1970s, we were doing a lot of work on local pollution, but then we kind of stepped back and all the issues of climate change – I was looking at papers. There are thousands of papers coming out each year. The actual number of papers coming out of thermal science is very, very small, but if you talk about how this energy imbalance comes about, what the greenhouse effect is, it's basically thermal sciences.
Safety and security, again, is a very major issue. I'm not talking just about politics and other terrorism activities and so on. I'm talking about fires, explosions, and many of those have come up and it has driven our research or should we be involved more, can we spearhead these issues. I mentioned here stand-alone systems, that's a fairly important idea that we can make systems which take you away from the grid and you are able to provide energy to remote areas. For instance, in India, and many other countries where you can provide energy to the local people and change the conditions completely. We do have three different needs. We have developed nations, which may worry about environment and safety. Then you have developing countries which worry about cost and supply and pollution and the under developed countries, which basically just want the standard of living to go up. They want to get the energy coming in.
|